JavaScript Object 생성
- 객체 리터럴
- new 키워드
- Prototype
- Object.create()
1. 객체 리터럴
중괄호 안에 이름과 값을 :으로 구분한 순서쌍을 쉼표로 연결한 List
var empty = {};
var point = {x:0, y:0};
var point2 = {x: point.x, y:point.y + 1}
var book = {
"main title" : "Javascript", // 공백도 가능
"for" : "all audiences"
}
console.log("empty : ", empty);
console.log("point : ", point);
console.log("point2 : ", point2);
2. new 키워드
var o = {};
var o2 = new Object();
// o 와 o2는 같다.
var a = new Array();
var d = new Date();
var r = new RegExp("js") // 패턴매칭을 위한 RegExp 객체3. prototype
Javascript 의 모든 객체는 또 다른 Javascript의 객체와 연관되어 있음.
이 두 번째 객체 : Prototype
객체는 Prototype으로부터 Property를 상속받는다.
- 객체 리터럴로 생성된 모든 객체는 Prototype 객체가 같다.
- Object.prototype으로 접근 가능
- new Array()는 Array.prototype을 객체의 프로토 타입으로 사용하는 식
- Object prototype : 프로토타입이 없음.
- 다른 객체들은 보통 prototype이 다 있음.
- Array.prototype은 Object.prototype을 상속받음.
- 위와 같은 걸 Prototype chain이라고 한다 .
4. Object.create()
create()
- 첫 번째 인자 : 프로토타입 객체
- 두 번째 인자 : 새 객체의 프로퍼티 정보 생략가능
var o1 = Object.create({x:1, y:2});
console.log(o1);
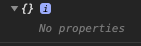
var o2 = Object.create(null);
console.log(o2);
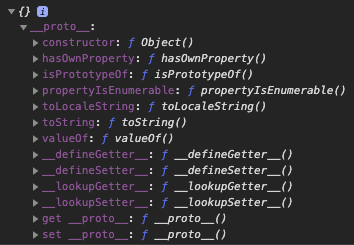
var o3 = Object.create(Object.prototype)
console.log(o3);
o1 :
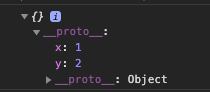
o2 : -> 어떠한 객체도 상속받지 않는다.

o3 : -> Object객체는 상속받고 싶을 때
inherit 함수 구현
상속 받도록 구현하지 않고 객체 자체를 인자로 넣어 Property를 추가하려 한다면,
기존에 있는 수정되어서는 안되는 Property를 수정하게 되는 실수를 할 수 있다.
Prototype을 이용한 상속으로 원하는 Property를 추가하면서도 그 실수를 방지하기 위해 inherit function을 구현해 사용한다.
function inherit(p) {
if (p == null) throw TypeError();
if (Object.create) // ECMAScript 5 이상에 정의되어 있음
return Object.create(p);
// Object.create 가 정의되어있지 않으면
var t = typeof p;
if (t !== "object" && t !== "function") {
throw TypeError();
}
function f() {};
f.prototype = p;
return new f();
}'웹 프로그래밍 > Javascript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Javascript Function (0) | 2020.06.24 |
|---|---|
| Javascript Scope, 변수 (0) | 2020.06.23 |
| Javascript Array (0) | 2020.06.23 |
| JavaScript Property (0) | 2020.06.21 |
| Javascript 세미콜론 (0) | 2020.05.30 |